In an era dominated by numbers and statistics, the stories behind consumer choices often remain hidden. Businesses that rely solely on charts and percentages may miss the crucial “why” behind customer actions. This article delves into the world of qualitative market research, revealing how in-depth exploration of attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors can transform raw data into actionable strategies.
Why Qualitative Insights Matter Beyond Numbers
While quantitative studies can quantify the frequency of a behavior or preference, they rarely answer questions about underlying motivations. Qualitative research is designed to probe deeper. By engaging directly with participants through conversations and observations, researchers uncover rich, contextual understanding of consumer experiences. These insights provide the narrative that informs better product development, targeted marketing, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Understanding the emotional and psychological drivers behind choices allows companies to anticipate evolving needs and refine offerings in a way that resonates on a personal level. Without these insights, strategies may lack authenticity and fail to connect with the target audience.
Key Methods and Techniques
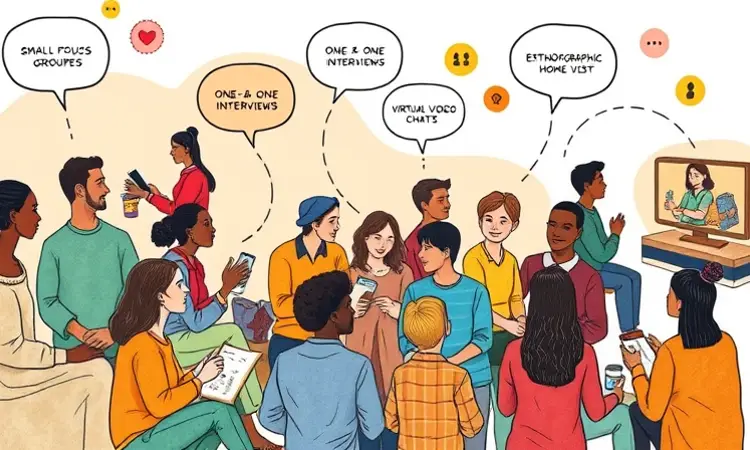
Qualitative research encompasses a variety of methods, each suited to different objectives and contexts. Selecting the appropriate technique is critical to gathering the depth of insight required.
- In-depth Interviews (IDIs): One-on-one conversations lasting 30 to 120 minutes, ideal for sensitive or complex topics where individual perspectives are essential.
- Focus Groups: Small groups of 6–8 participants discussing guided topics for 60 to 120 minutes, useful for exploring group dynamics and spontaneous reactions.
- Ethnography and Observational Studies: Immersive sessions where researchers observe participants in real-world environments, capturing unfiltered behaviors and contexts.
- Projective Techniques: Storytelling, image association, and creative exercises that bypass conscious filters and reveal subconscious attitudes.
- Content Analysis: Thematic review of social media posts, reviews, and open-ended survey responses to identify recurring patterns and sentiments.
Comparing Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches
Both qualitative and quantitative methods have unique strengths. When used together, they offer a comprehensive view of the market.
This side-by-side comparison highlights how qualitative research adds nuance and meaning to numeric findings, guiding more informed decision-making.
Core Applications and Use Cases
Organizations across industries leverage qualitative methods to solve a variety of challenges.
- Product Development: Ethnographic studies and IDIs uncover unmet needs and shape prototypes based on real-life usage.
- Brand Perception: Focus groups and projective techniques reveal emotional associations and help refine messaging.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Shop-alongs and diary studies identify friction points and optimize touchpoints across channels.
- Advertising Concept Testing: Creative workshops gauge reactions to ad storyboards, slogans, and visuals before launch.
- User Experience (UX) Research: In-home testing and usability walkthroughs improve digital products, interfaces, and services.
Case Study Example: A leading laundry brand conducted online focus groups with 50 participants to iteratively refine its packaging design. By observing reactions to color schemes and label layouts, the team increased packaging appeal by 35% in subsequent consumer tests.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
Innovation continues to reshape qualitative research, making it more efficient and expansive.
Online platforms like UserTesting and Lookback enable remote IDIs and virtual focus groups, reducing costs and geographic constraints. These tools offer video recording, screen sharing, and AI-driven transcription to streamline analysis.
Meanwhile, AI-driven sentiment analysis and natural language processing extract themes and emotions from large text datasets, accelerating thematic coding. However, human expertise remains essential to interpret subtleties and cultural contexts that machines may overlook.
Blended research platforms are emerging, fusing quantitative dashboards with qualitative narratives in a single view. This integration allows stakeholders to toggle between data streams, exploring numbers and stories side by side.
Implementing Qualitative Research: Best Practices
Effective qualitative research requires careful planning and execution. Adhering to best practices ensures reliability and actionable outcomes.
- Define Clear Objectives: Articulate specific research questions and avoid ambiguous goals that dilute focus.
- Choose Skilled Moderators: Select facilitators with deep domain knowledge and strong interpersonal skills to manage dynamics and probe sensitively.
- Ensure Diverse Participant Profiles: Recruit a varied mix of demographics and psychographics to capture a wide range of perspectives.
- Iterate and Integrate: Use qualitative findings to refine quantitative surveys, and vice versa, for continuous learning.
- Maintain Ethical Standards: Obtain informed consent, protect privacy, and mitigate biases throughout the process.
Challenges, Limitations, and Complementary Roles
Despite its strengths, qualitative research has inherent limitations that must be acknowledged:
Generalizability is restricted due to small, non-random samples, making it unsuitable for statistical validation. Moderator and interpretation biases can influence findings, requiring rigorous checks such as interviewer training and peer debriefs.
Rather than replacing quantitative methods, qualitative research serves as a complementary tool. It excels at uncovering the nuances that inform survey design, hypothesis generation, and contextualized data interpretation.
By combining both methodologies in a mixed-methods framework, organizations gain a 360-degree view of their market, ensuring strategies are both data-driven and human-centered.
Conclusion
Qualitative market research transcends the limitations of charts and graphs by tapping into the human stories behind consumer decisions. Its rich narratives and contextual details breathe life into numbers, revealing hidden opportunities and guiding strategic innovation.
As technology advances, the synergy between AI tools and traditional methods promises to enhance efficiency without sacrificing depth. By mastering qualitative approaches, businesses can stay attuned to evolving consumer needs and cultivate lasting connections built on understanding and empathy.
Ultimately, looking beyond the charts empowers organizations to craft offerings that resonate emotionally, fostering loyalty and driving sustainable growth in an increasingly complex marketplace.